The Status Commands
Monitoring the status of your studies is made accessible with two commands in Merlin: merlin status and merlin detailed-status. The Status Command offers a summary of your entire study's status, while The Detailed-Status Command provides task-specific information that can be further filtered as needed.
How They Work
As your study is progressing, Merlin will create MERLIN_STATUS.json files for each step behind the scenes. When states are modified, so are the
MERLIN_STATUS.json files. The merlin status and merlin detailed-status commands will read from these files and format the output in an easy-to-analyze manner.
For steps that contain samples, a MERLIN_STATUS.json file is created for each sample that's ran. As sets of samples finish running, Merlin will condense all of the MERLIN_STATUS.json files in that set of samples into one MERLIN_STATUS.json file. This helps to save space in the file system for all of the other important outputs that your studies provide.
The format of a MERLIN_STATUS.json file is as follows:
{
"step_name": {
"parameters": {
"cmd": {
"TOKEN1": "value1",
"TOKEN2": "value2",
.
.
.
},
"restart": {
"TOKEN1": "value1",
"TOKEN2": "value2",
.
.
.
}
},
"task_queue": "name_of_queue", // (1)
"worker_name": "name_of_worker",
"step_workspace": {
"status": "<One of the 7 possible statuses>", // (2)
"return_code": "<One of the 8 possible return codes>", // (3)
"elapsed_time": "xd:xxh:xxm:xxs",
"run_time": "xd:xxh:xxm:xxs",
"restarts": <integer>
}
}
}
- If you run your study locally, there will not be any entries for
task_queueandworker_name. - See Possible Statuses below for more information.
- See Possible Return Codes below for more information.
In the parameters section here, the cmd parameters are parameters used in the cmd key of the run property in a step, and the restart parameters are parameters
used in the restart key of the run property in a step. Both of these values may be null if no parameters are used in either key.
If your step uses samples, a "step_workspace" entry for each sample will be created. In other words, you will have multiple "step_workspace" entries of the form "step_workspace/00", "step_workspace/01", "step_workspace/02", etc.
MERLIN_STATUS.json Format With Samples
Say we have a workflow that generates 3 samples and a step named just_samples that utilizes them. This would result in a MERLIN_STATUS.json file that looks like so:
{
"just_samples": {
"parameters": {
"cmd": null,
"restart": null
},
"task_queue": "just_samples_queue",
"worker_name": "sample_worker",
"just_samples/00": {
"status": "FINISHED",
"return_code": "MERLIN_SUCCESS",
"elapsed_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"run_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"restarts": 0
},
"just_samples/01": {
"status": "FINISHED",
"return_code": "MERLIN_SUCCESS",
"elapsed_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"run_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"restarts": 0
},
"just_samples/02": {
"status": "FINISHED",
"return_code": "MERLIN_SUCCESS",
"elapsed_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"run_time": "0d:00h:00m:00s",
"restarts": 0
}
}
}
Possible Statuses
Note
The INITIALIZED and RUNNING states do not have a colorblind symbol since they do not appear in the progress bar, just in the summary section of a step.
Note
Colors here are chosen based on Bang Wong's optimized color palette for color-blind individuals.
During the execution process of your step, there are 7 possible statuses that a task may hold:
| Status | Description | Color | Colorblind Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
INITIALIZED |
Tasks in the INITIALIZED state have been queued but have not began processing yet |
light-blue #56b3e9 |
N/A |
RUNNING |
Tasks in the RUNNING state have began executing but have not yet entered a completed state ("completed states" are any of the states listed below) |
blue #0072b2 |
N/A |
FINISHED |
Tasks in the FINISHED state have successfully ran to completion |
green #009e74 |
█ |
CANCELLED |
Tasks in the CANCELLED state have exited with the $(MERLIN_STOP_WORKERS) exit code (see Step Return Variables) |
yellow #f0e442 |
/ |
FAILED |
Tasks in the FAILED state have exited with the $(MERLIN_SOFT_FAIL) or $(MERLIN_HARD_FAIL) exit codes (see Step Return Variables) |
red #d55e00 |
⣿ |
DRY_RUN |
Tasks in the DRY_RUN state have successfully run in the Dry Run mode | orange #e69f00 |
\ |
UNKNOWN |
Tasks in the UNKNOWN state have exited with an unknown return code |
green #666666 |
? |
Possible Return Codes
Note
The return codes here follow almost directly from the Step Return Variables. Only the MERLIN_DRY_SUCCESS nad MERLIN_UNRECOGNIZED return codes are unique here.
Once a task has completed running, there are 8 possible return codes that it could have:
| Return Code | Description |
|---|---|
MERLIN_SUCCESS |
This task finished successfully |
MERLIN_SOFT_FAIL |
This task failed but not badly enough to stop the workflow entirely |
MERLIN_HARD_FAIL |
This task failed and we now need to stop the entire workflow |
MERLIN_RESTART |
This task needs restarted; Next run will run the "restart" command in the step unless it's undefined |
MERLIN_RETRY |
This task needs to be retried; Will automatically re-run the "cmd" for the step |
MERLIN_STOP_WORKERS |
This task exited with a code to stop the workers |
MERLIN_DRY_SUCCESS |
This task successfully completed in the Dry Run mode |
MERLIN_UNRECOGNIZED |
This task finished with an unrecognized return code |
Inputs
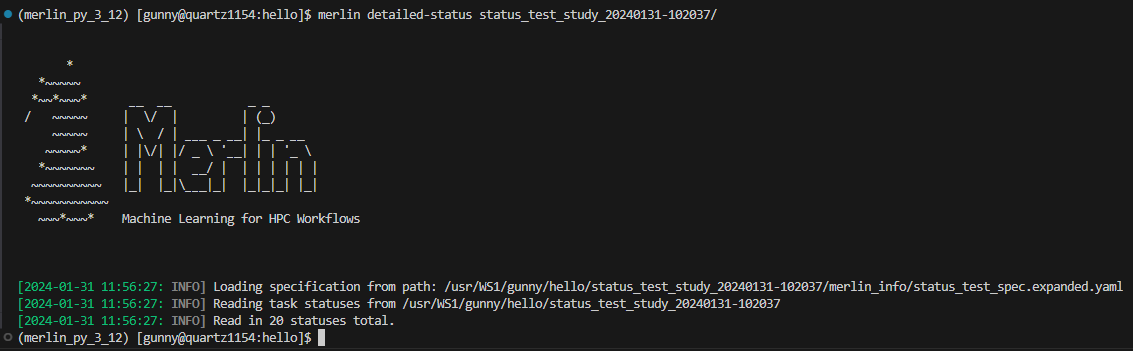
Both the merlin status and the merlin detailed-status commands can take either a yaml spec file or an output workspace as input.
Example
Say we have a spec file hello_world.yaml that we've ran which created an output workspace hello_world_20230503-105137/. We can check the status of our study with either option.
If you choose to provide an output study directory as input, Merlin will pull information from the expanded spec file located in the
merlin_info/ directory.
Tip
If you're not familiar with the merlin_info/ directory, check out The Basics of Interpreting Output to learn more.
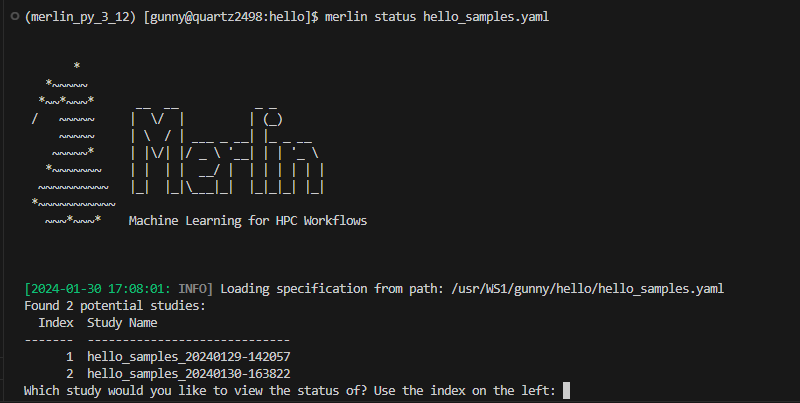
If you choose to provide a spec file as input, Merlin will search the OUTPUT_PATH (see Reserved Variables for more info on this variable) for possible studies associated with this spec. If there are multiple output directories associated with your spec file, then you will be prompted to select which study you'd like to view the status of, as is shown in the figure below.
If you'd like to ignore this prompt, you can use the --no-prompts option. This will automatically select the most recent study for you.
Usage:
The Status Command
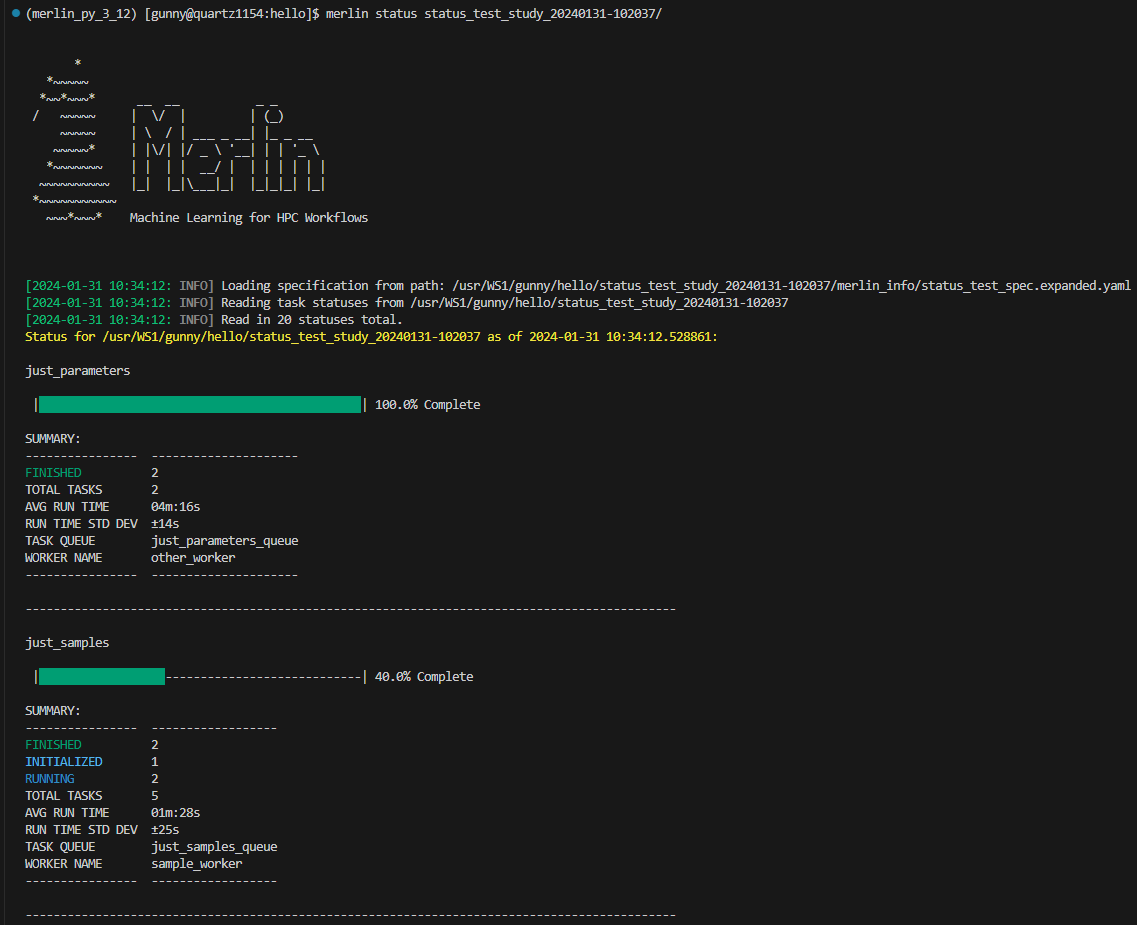
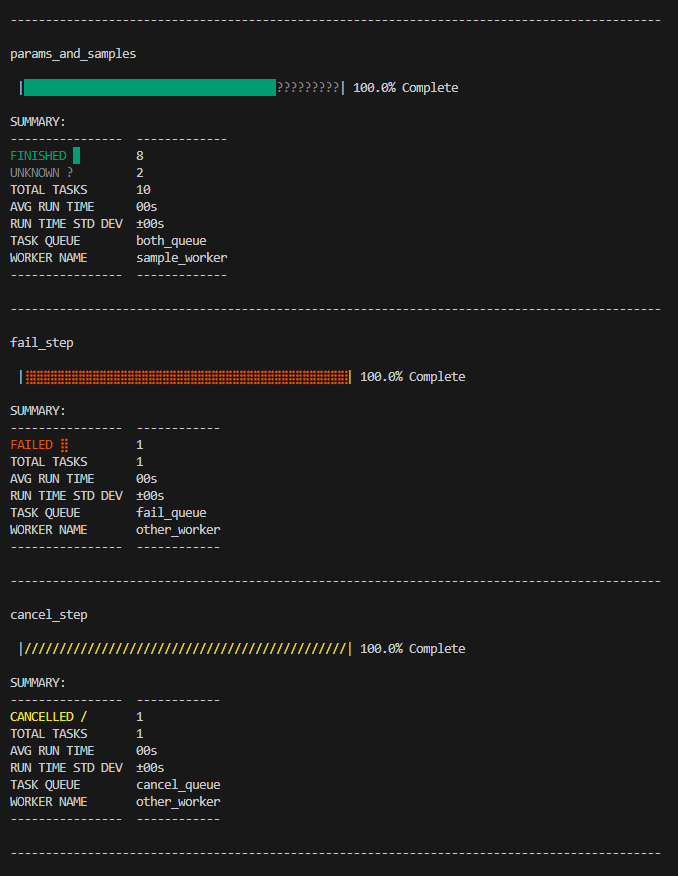
The merlin status command is designed to help you see the overall status of your entire study. It provides you a step-by-step view with progress bars and summary tables that will show you exactly how many tasks are in each state, how many tasks in total there are for a step, the average & standard deviation of the run times for tasks in a step, and which workers & task queues each step is associated with (if applicable).
This command requires you to select a study to view the status of. For more information on inputs to this command see Inputs above.
Usage:
To help assist with colorblindness, Merlin provides the --cb-help option for the status command. This option will add symbols to the progress bar for different task statuses.
Usage:
Example Colorblind-Assisted Status Output
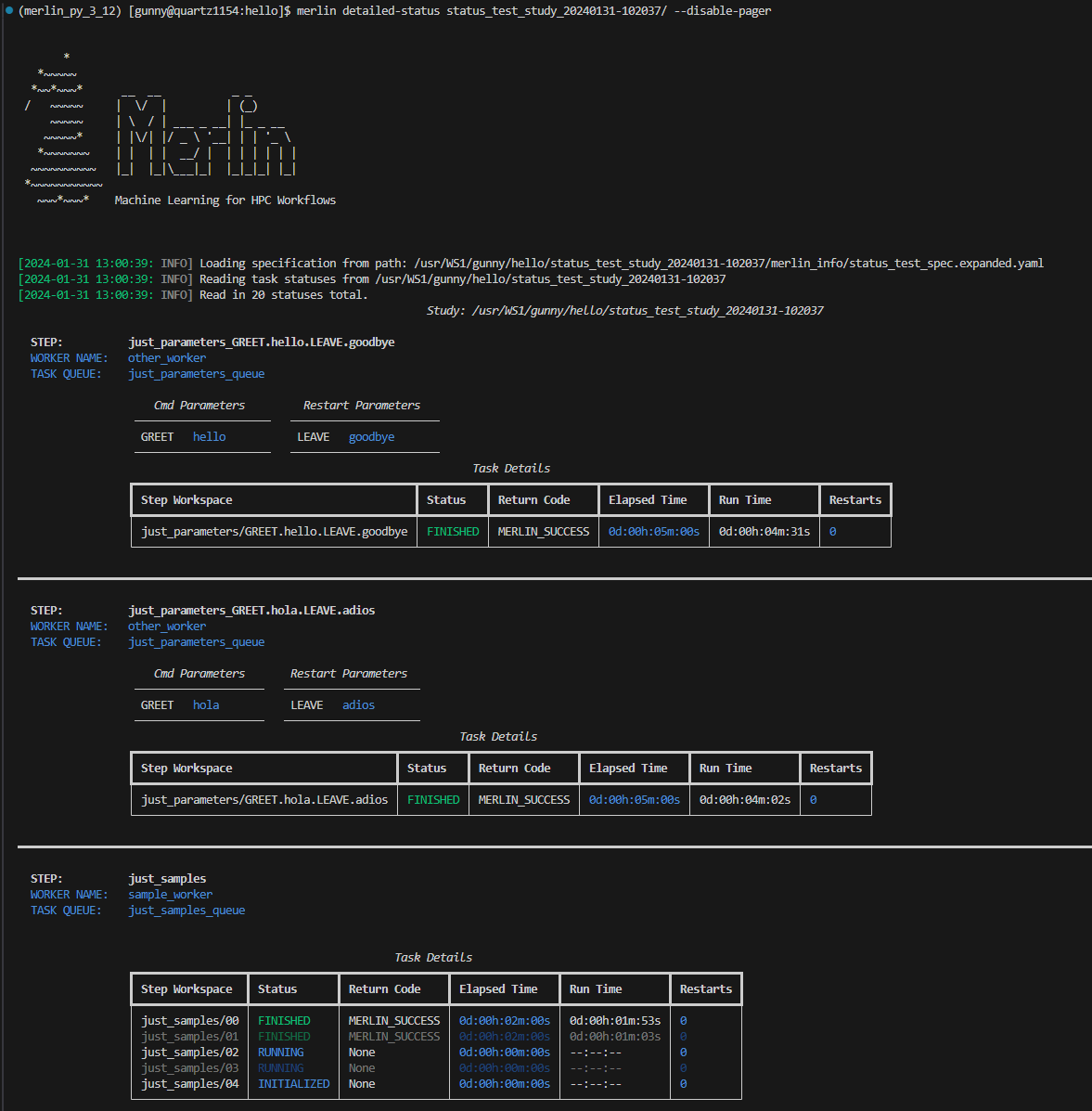
The Detailed-Status Command
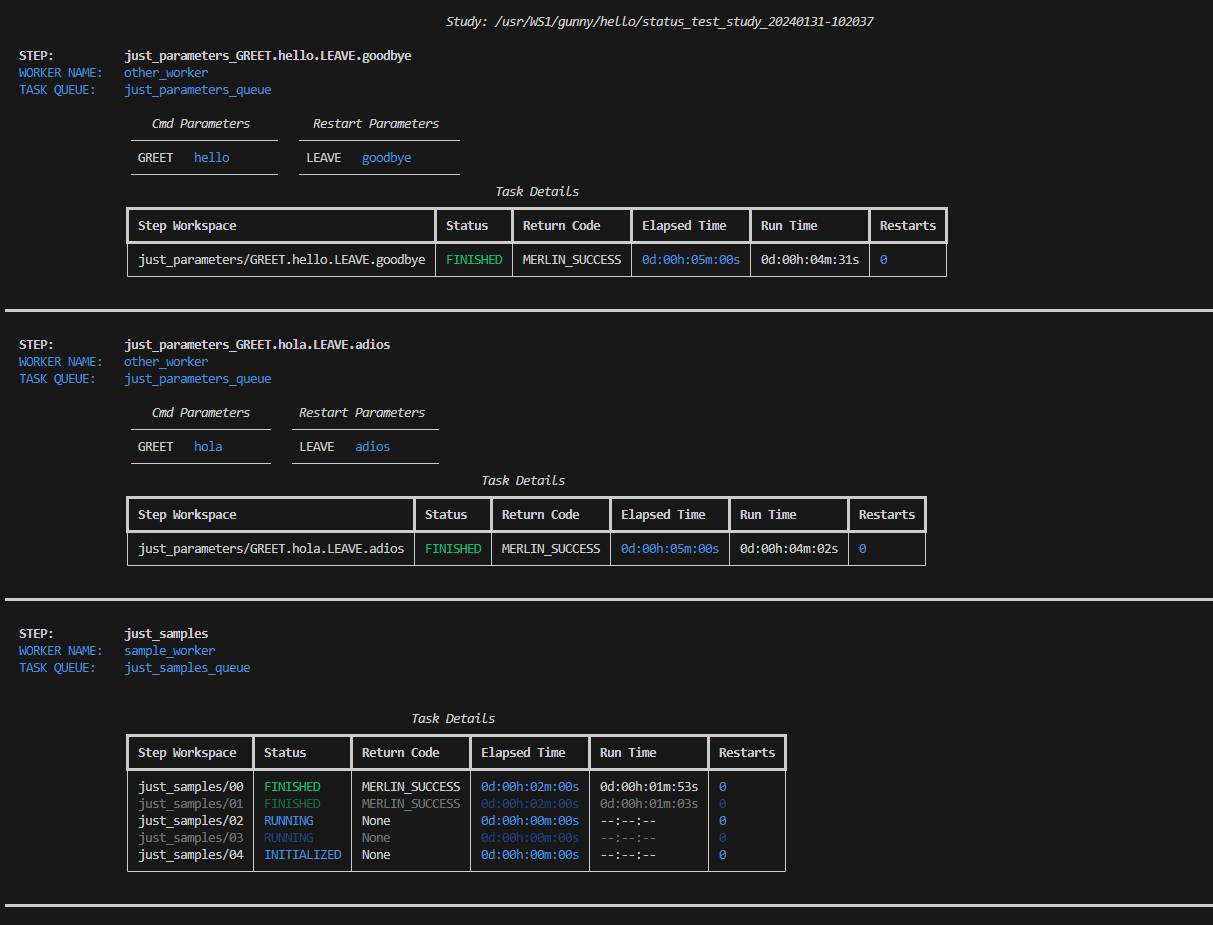
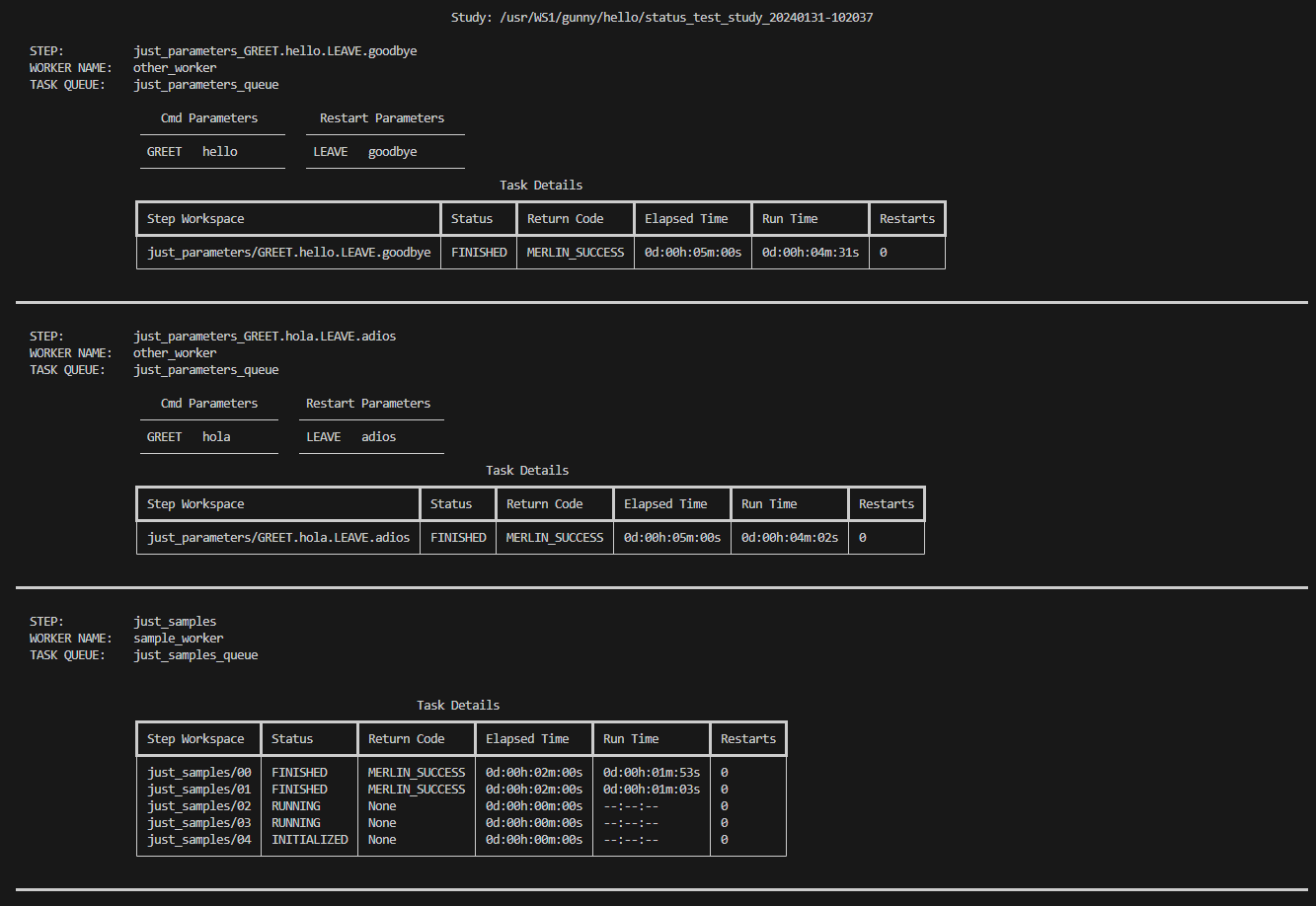
The merlin detailed-status command is designed to help you see an in-depth status breakdown of each step in your study. It provides a task-by-task view with each task's workspace, status, return code, elapsed time, run time, and number of restarts available for you to see.
This command requires you to select a study to view the status of. For more information on inputs to this command see Inputs above.
Manpager Note
If the output of the detailed-status command looks something like this:
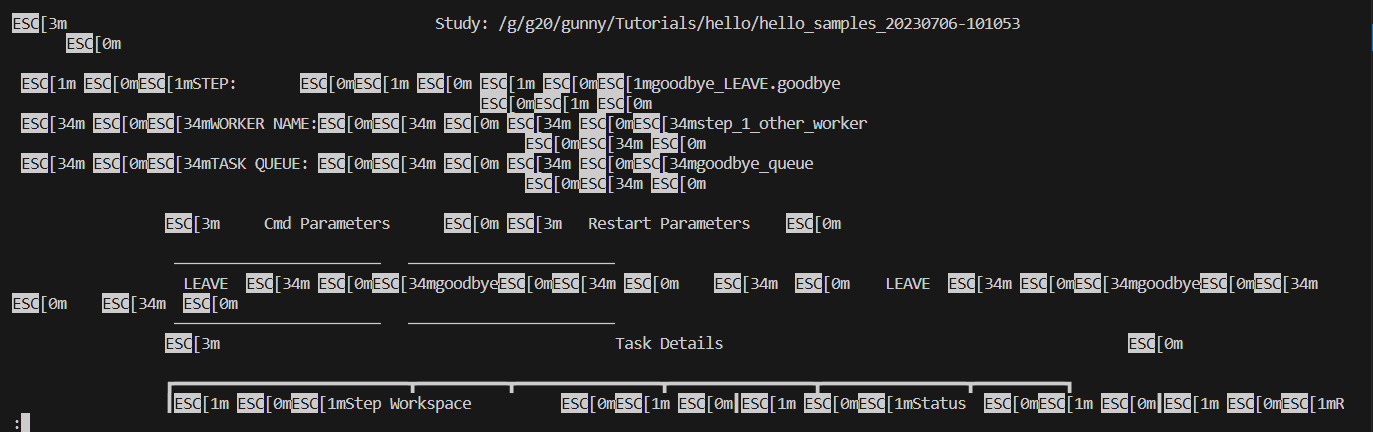
Then there are a couple things you can try to fix this problem:
-
Set the
MANPAGERorPAGERenvironment variable to be "less -r" and run again -
If the error isn't fixed after 1. above, then:
a. You can disable the theme with the
--disable-themeoption (see Disable Theme below).b. If you'd rather not disable the theme, the error usually stems from using the pager functionality, so you can try disabling that with the
--disable-pageroption (see Disable Pager below). Caution: you may end up outputting a lot of information to the shell all at once when using this option.
By default, the merlin detailed-status command will pull up a pager window containing the status information that was requested. Merlin uses this pager functionality to ensure we don't overload the shell by displaying too many task statuses at one time.
Usage:
To see all of the options that can be used with the pager, press h. To exit the pager, press q.
Once you close the pager, the statuses you requested will not appear and you'll be redirected back to your normal shell view.
Example Detailed-Status Output Once Pager Is Closed
Display Options
The merlin status command comes equipped with four options to help modify the display output: --disable-pager, --disable-theme, --layout, and --no-prompts. These options can all be used together or by themselves.
Disable Pager
Warning
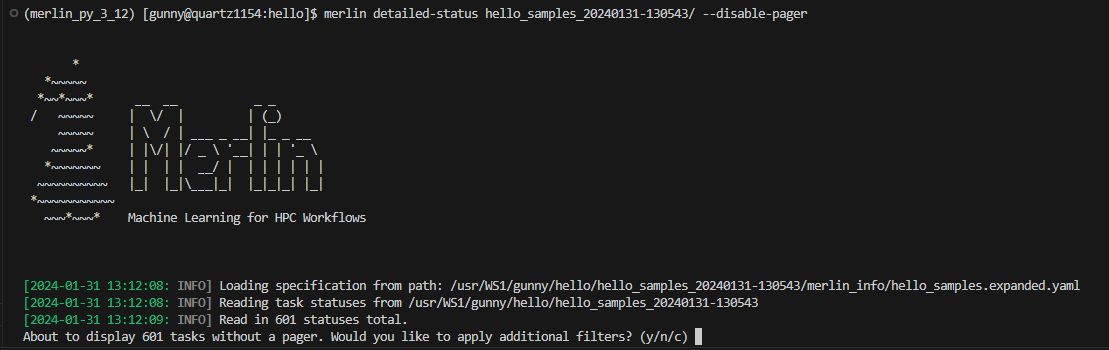
The --disable-pager option could cause you to unintentionally output thousands of task statuses to stdout, which may overload the shell with output. Merlin tries to help prevent this with prompts for additional filters but you should still use caution.
The --disable-pager option allows you to turn off the pager functionality that is on by default. This will redirect the detailed-status output to stdout rather than the pager.
Usage:
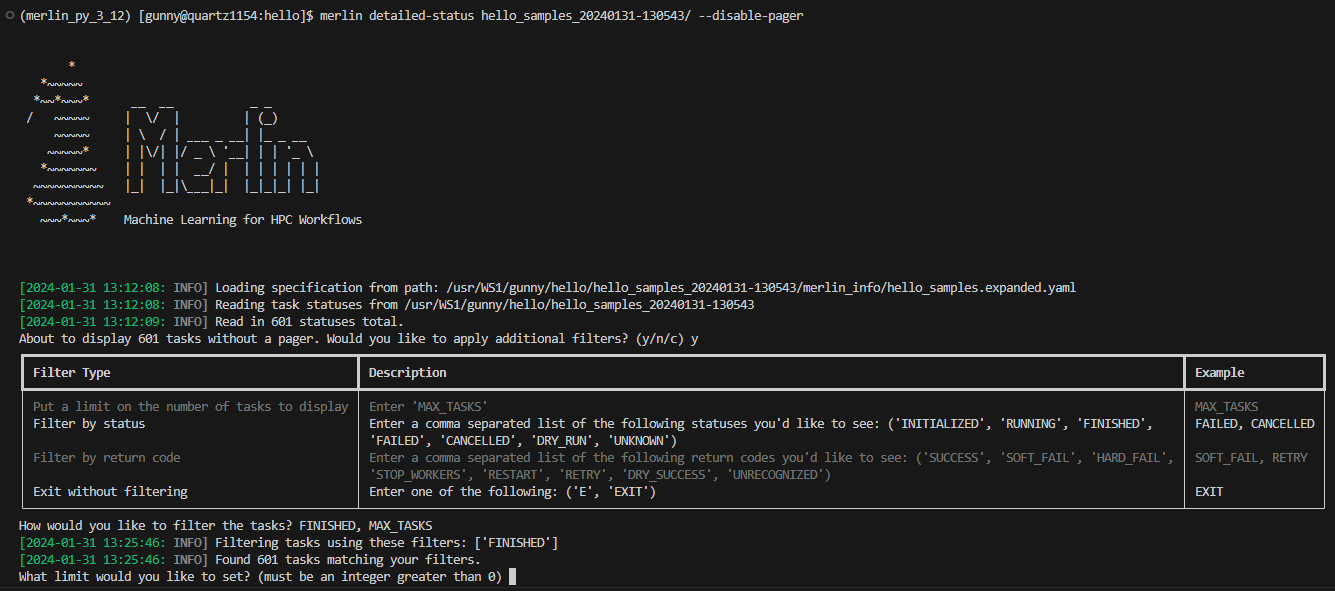
When using this option you may unintentionally output a lot of information to the shell which could cause problems. To help prevent issues from too much information being printed, Merlin will prompt you to further filter your output if there are more than 250 task statuses to display:
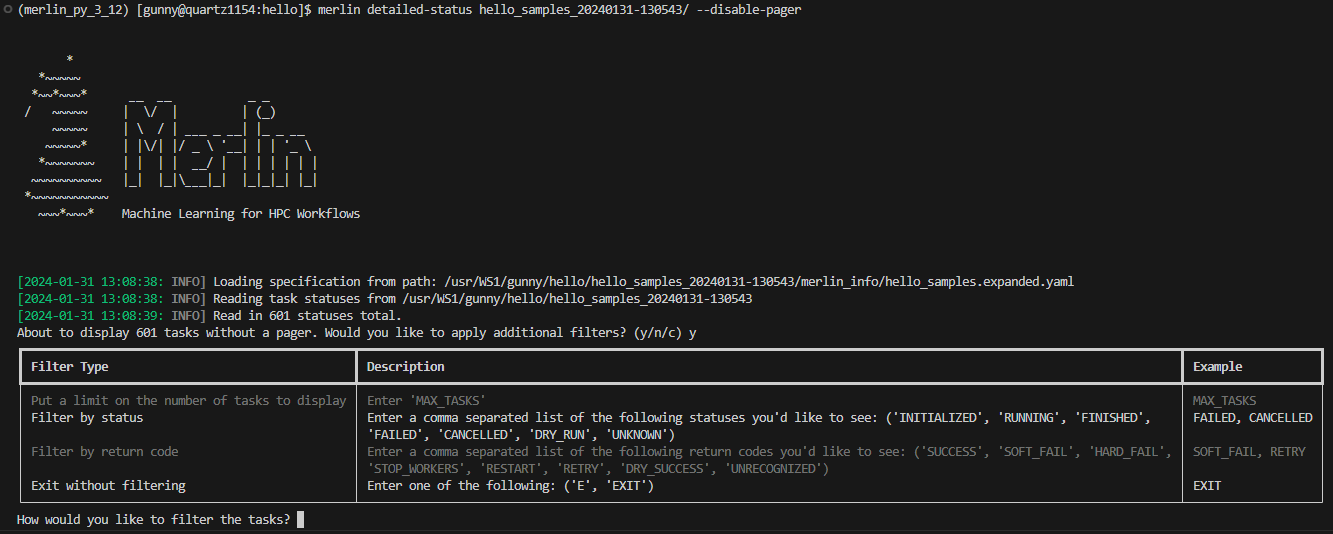
If you'd like to cancel the filter and the display entirely, press c. If you don't wish to filter and just want to display your tasks, press n (again, be cautious when using this option). If you decide that filtering your tasks would be a better option, press y and you'll see the following filter options:
Note
If you put E or EXIT anywhere in the prompt, no filters will be applied and you'll be returned to the original prompt. For example, entering FAILED, E, CANCELLED will return you to the original prompt without filtering anything.
Here, the filters are equivalent to certain Filter Options:
- Limiting the number of tasks to display =
--max-tasks - Filtering by status =
--task-status - Filtering by return code =
--return-code
It's possible to combine different filter types here. For example, a valid filter could be FAILED, STOP_WORKERS which would show any tasks with a FAILED status and any tasks with a STOP_WORKERS return code.
If you put MAX_TASKS anywhere in your filter, you'll receive another prompt asking you for an integer greater than 0 to set as the limit on the number of tasks to display:
Disable Theme
The --disable-theme option allows you to disable the color scheme used in the output of the detailed-status command.
Usage:
Layout
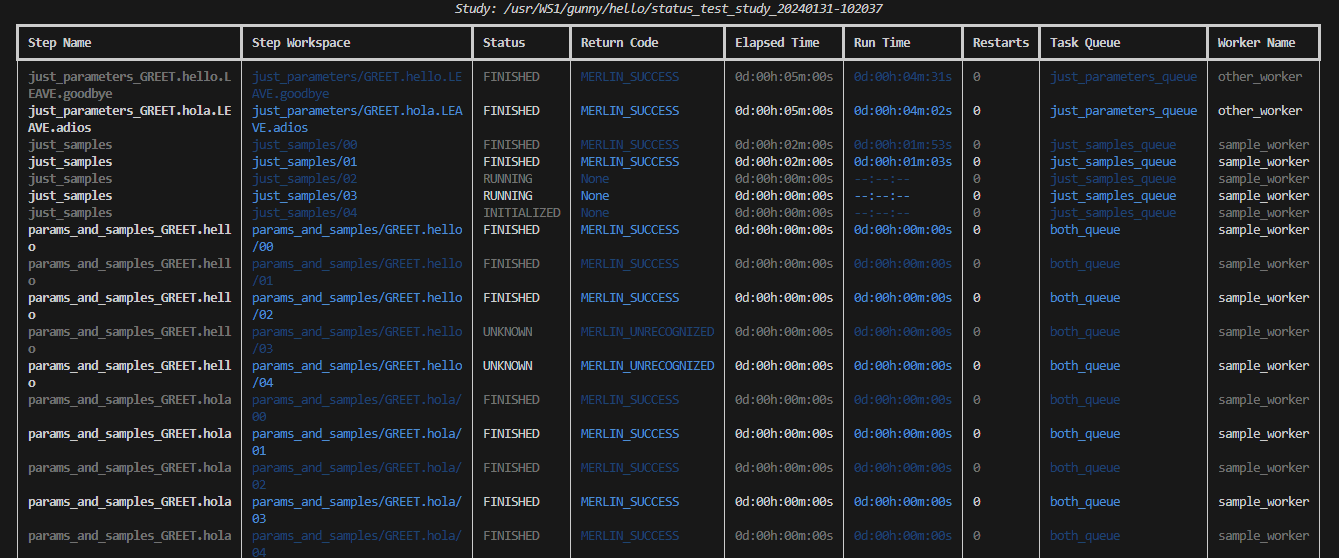
By default, the merlin detailed-status command displays tasks on a step-by-step basis. To change this and group all of the tasks together, you can use the --layout table option.
Usage:
No Prompts
Warning
Be cautious when using this option with the --disable-pager option. You may accidentally output thousands of task statuses to the shell.
The --no-prompts option is an option to disable any prompts that might be displayed while using the detailed-status command. There are four possible ways to use this filter, each with a slightly different result:
- Used with a workspace as input: Nothing will happen here as there will be no prompts asking to select a study and no prompts asking you to filter tasks
- Used with a spec as input: Instead of prompting you to select a study, the most recent study will automatically be selected
- Used with a workspace as input and the
--disable-pageroption enabled: Any prompt that may have been displayed asking you to filter your output will be ignored - Used with a spec as input and the
--disable-pageroption enabled: The most recent study will automatically be selected and any prompt that may have been displayed asking you to filter your output will be ignored
Usage:
Filter Options
There are six filter options with the detailed-status command: --max-tasks, --return-code, --steps, --task-queues, --task-status, and --workers. These filters can be used together or by themselves.
Note
In the images that are in the sections below, the --disable-pager filter is used. This is simply to show all of the output of the detailed-status filters in one place. It is not required (nor is it recommended) when using the filter options.
If you don't use the --disable-pager option but you get strange ASCII characters in the output of the pager, see the "Manpager Note" above above for instructions on how to fix that.
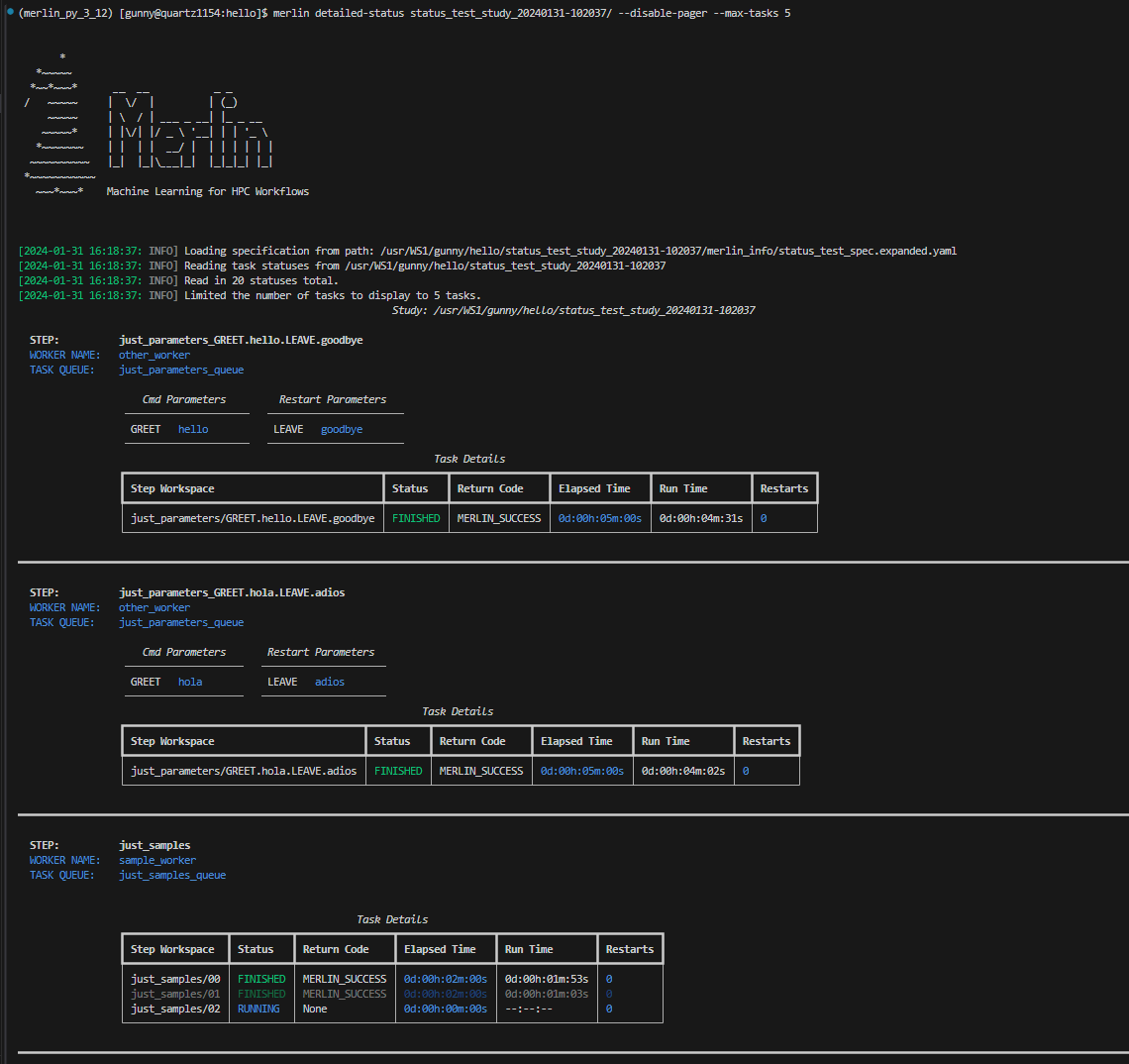
Max Tasks
The --max-tasks filter allows you to limit how many tasks are displayed in the output. This filter takes in an integer as input which represents the maximum number of tasks you'd like to display.
Usage:
Example Detailed-Status Output With Max Tasks Filter
Here, we're setting the maximum number of tasks that can be displayed to 5:
Return Code
The --return-code filter allows you to search for tasks with a certain return code. This filter can take one or more return codes as input. Valid inputs include: SUCCESS, SOFT_FAIL, HARD_FAIL, STOP_WORKERS, RESTART, RETRY, DRY_SUCCESS, and UNRECOGNIZED.
Usage:
Example Detailed-Status Output With Return Code Filter
Here, we're asking to see all tasks that completed with a SOFT_FAIL return code:
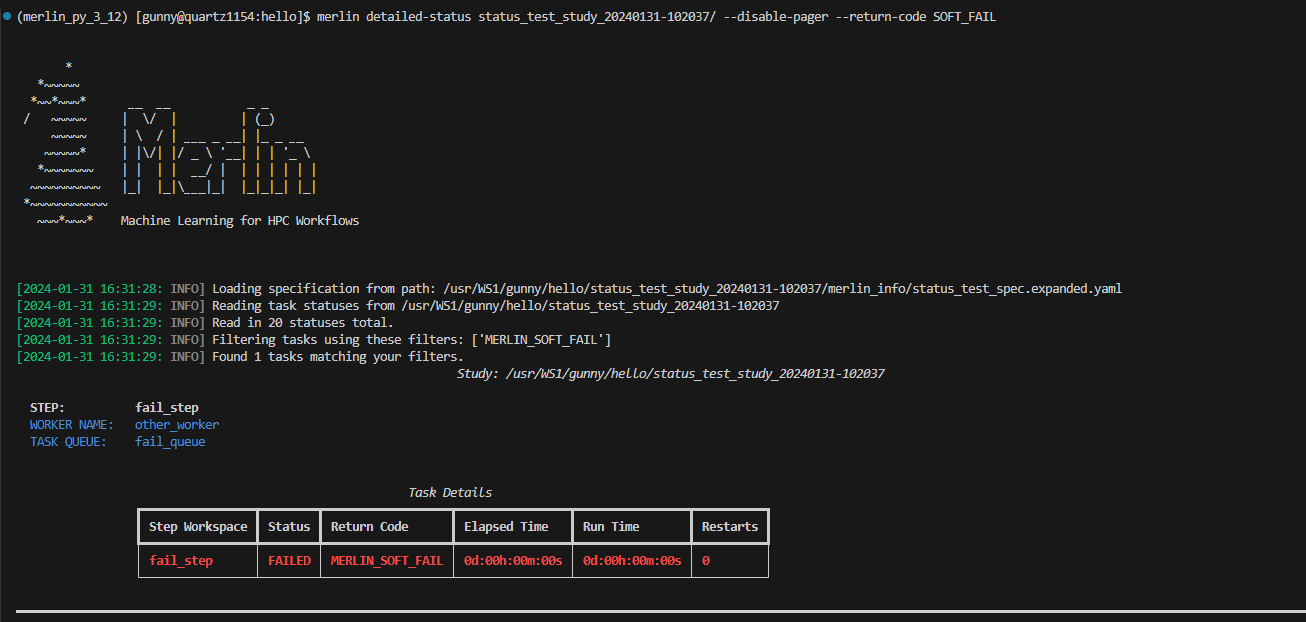
Steps
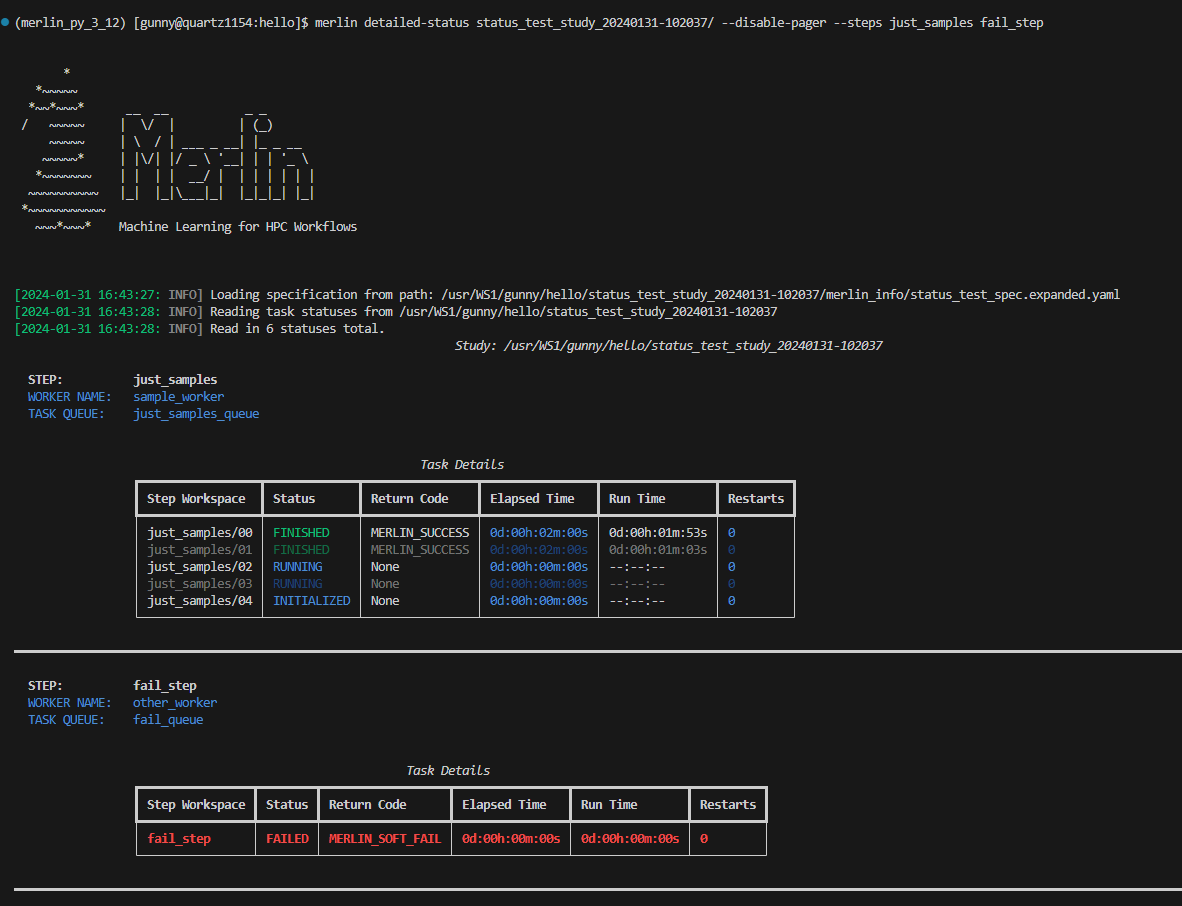
The --steps filter allows you to view status information about specific steps. This flag can take one or multiple steps as input. If a step provided cannot be found, that step will be removed from the filter.
Usage:
Example Detailed-Status Output With Steps Filter
Here, we're asking to see all task statuses from the just_samples and fail_step steps:
Task Queues
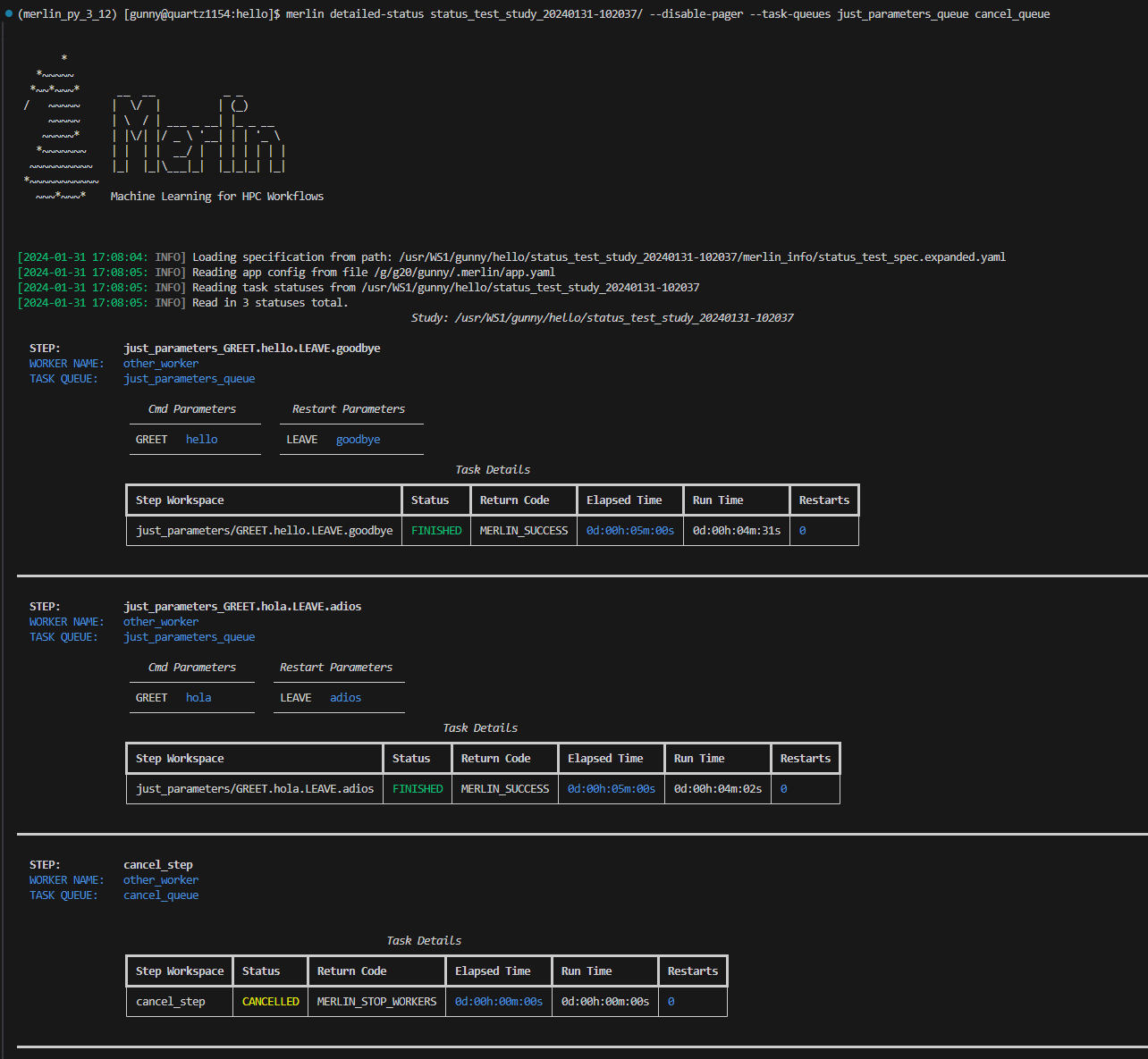
The --task-queues filter allows you to view statuses of tasks in certain task queues. This filter can take one or more queues as input. If a queue provided cannot be found, that queue will be removed from the filter.
Usage:
merlin detailed-status <spec or output directory> --task-queues <space-delimited list of task queues>
Example Detailed-Status Output With Task Queues Filter
Here, we're asking to see all task statuses of tasks in the just_parameters_queue and cancel_queue queues:
Task Status
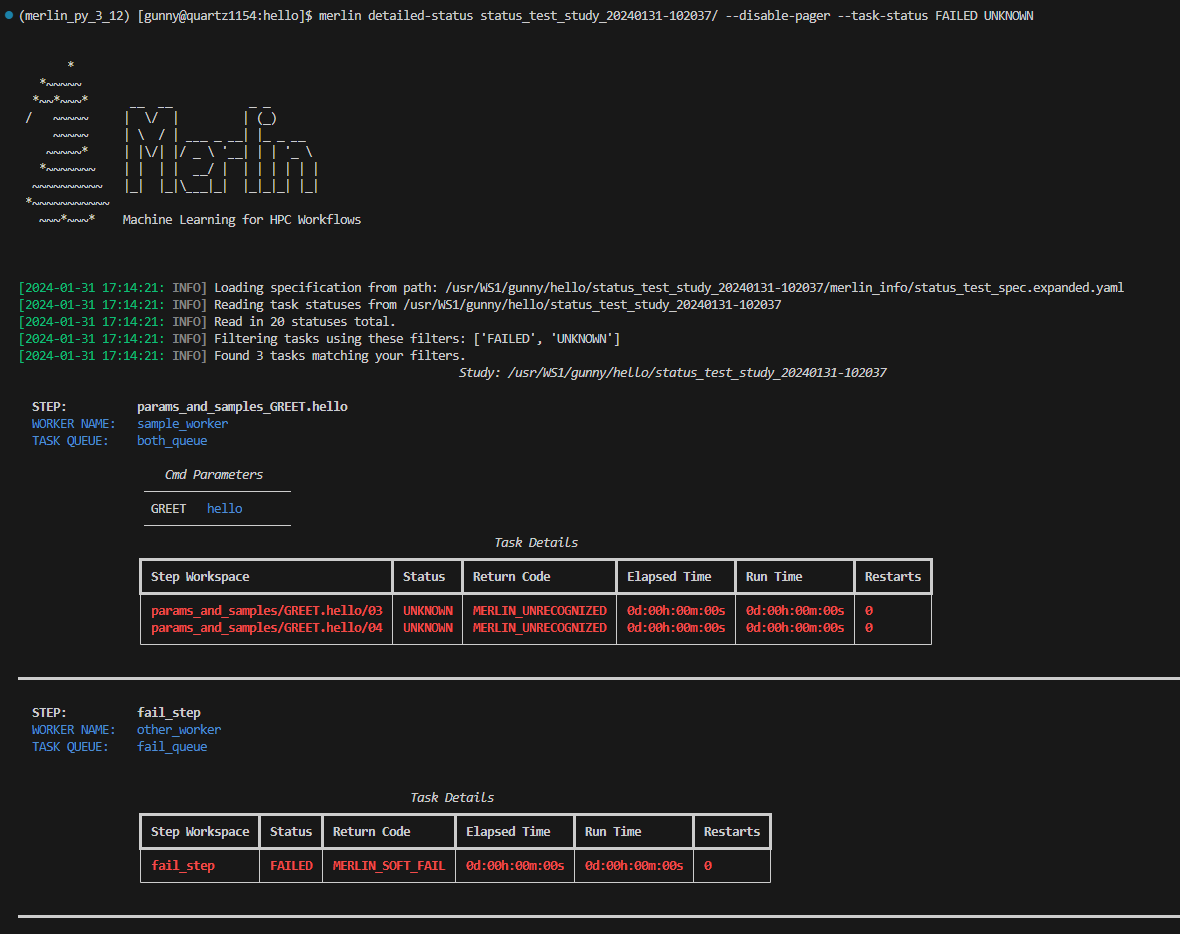
The --task-status filter allows you to search for tasks with a certain status. This filter can take one or more statuses as input. Valid inputs include: INITIALIZED, RUNNING, FINISHED, FAILED, CANCELLED, DRY_RUN, and UNKNOWN.
Usage:
merlin detailed-status <spec or output directory> --task-status <space-delimited list of task statuses>
Example Detailed-Status Output With Task Status Filter
Here, we're asking to see all task statuses that have a FAILED or UNKNOWN status:
Workers
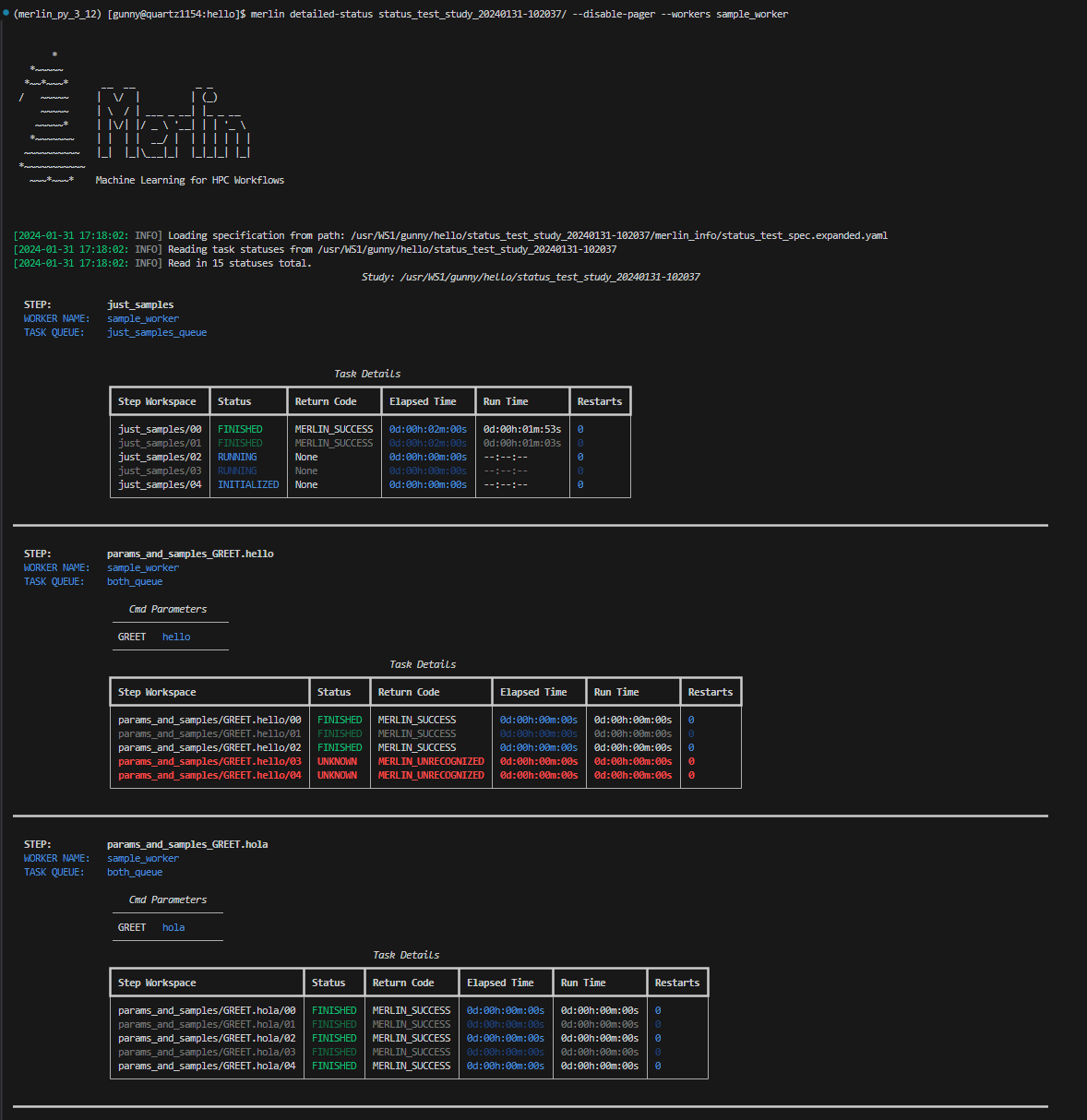
The --workers filter allows you to search for tasks that are being run or were ran by certain celery workers. This filter can take one or more worker names as input. If a worker provided cannot be found, that worker will be removed from the filter.
Usage:
Example Detailed-Status Output With Workers Filter
Here, we're asking to see all task statuses for tasks ran by the sample_worker worker:
Dumping Status Info to Output Files
Both status commands in Merlin allow you to dump to an output file. This output file must be either a .csv or a .json file.
When dumping to a file that does not yet exist, Merlin will create that file for you and populate it with the requested status info.
When dumping to a file that does exist, Merlin will append the requested status information to that file. You can differentiate between separate dump calls by looking at the timestamps of the dumps. For CSV files this timestamp exists in the time_of_status column (see Status CSV Dump Format below) and for JSON files this timestamp will be the top level key to the status entry (see Status JSON Dump Format below).
If you use the --dump option with merlin detailed-status and don't provide any filters, this will provide the same output in the file you're dumping to as it would if you used --dump with merlin status.
If you use the --dump option with merlin detailed-status and you do provide filters, only the statuses that match your filters will be written to the dump file.
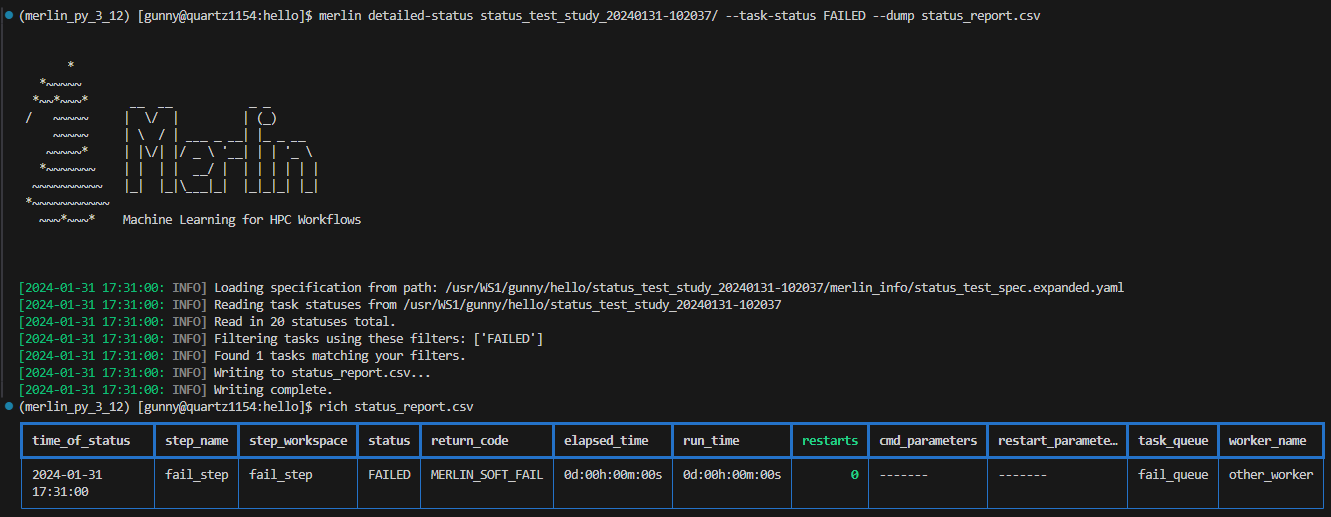
CSV Dump Format
The format of a CSV dump file for statuses is as follows:
time_of_status,step_name,step_workspace,status,return_code,elapsed_time,run_time,restarts,cmd_parameters,restart_parameters,task_queue,worker_name
The image below shows an example of dumping the status info of tasks with FAILED task statuses to a CSV file, and then displaying that CSV file using the rich-cli library:
JSON Dump Format
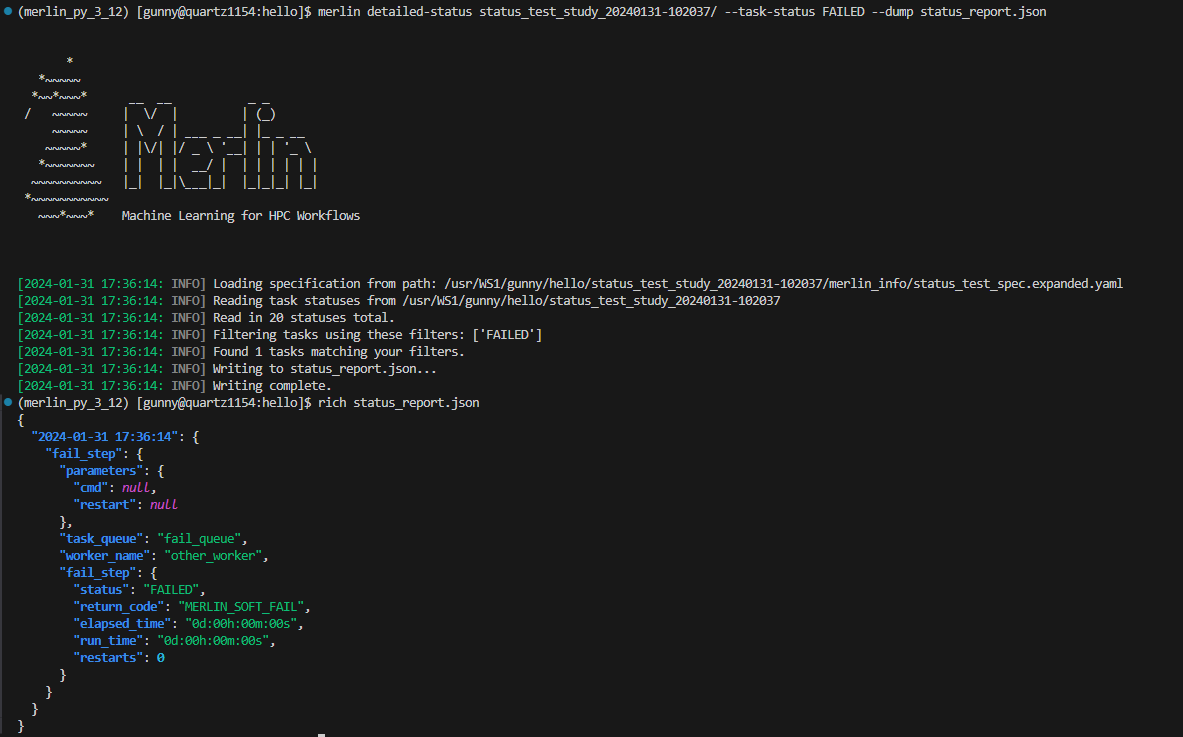
The format of a JSON dump file for statuses is almost exactly the same as the format of the MERLIN_STATUS.json files. The only difference is that each entry begins with a date:
{
"YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS": {
"step_name": {
"parameters": {
"cmd": {
"TOKEN1": "value1",
"TOKEN2": "value2",
"etc": "etc"
},
"restart": {
"TOKEN1": "value1",
"TOKEN2": "value2",
"etc": "etc"
}
},
"task_queue": "name_of_queue",
"worker_name": "name_of_worker",
"step_workspace": {
"status": "<One of the 7 possible statuses>",
"return_code": "<One of the 8 possible return codes>",
"elapsed_time": "xd:xxh:xxm:xxs",
"run_time": "xd:xxh:xxm:xxs",
"restarts": <integer>
}
}
}
}
The image below shows an example of dumping the status info of tasks with FAILED task statuses to a JSON file, and then displaying that JSON file using the rich-cli library:
Output Path and Task Server Options
The --output-path (or -o for short) option allows users to specify a new output path to search for studies in. This option is useful only when a spec is provided as the input. If this option is used when an output workspace is passed as input then it will be ignored.
Usage:
Example Usage of the --output-path Option
Say we have the following study with an OUTPUT_PATH variable defined to be the current working directory:
description:
name: hello_samples
description: a very simple merlin workflow, with samples
env:
variables:
N_SAMPLES: 3
OUTPUT_PATH: .
global.parameters:
GREET:
values : ["hello","hola"]
label : GREET.%%
study:
- name: step_1
description: say hello
run:
cmd: |
echo "$(GREET), $(NAME)!"
- name: step_2
description: print a success message
run:
cmd: print("Hurrah, we did it!")
depends: [step_1_*]
shell: /usr/bin/env python3
merlin:
resources:
workers:
demo_worker:
args: -l INFO --concurrency=1
steps: [all]
samples:
generate:
cmd: python3 $(SPECROOT)/make_samples.py --filepath=$(MERLIN_INFO)/samples.csv --number=$(N_SAMPLES)
file: $(MERLIN_INFO)/samples.csv
column_labels: [NAME]
Running this normally with:
creates a hello_samples_<timestamp>/ output workspace in the current working directory. However, if we ran this with:
This would create a hello_samples_<timestamp>/ output workspace in a directory called studies/ without modifying the original hello_samples.yaml file.
In other words, we'd now have the following directory structure in our current working directory:
current_working_dir/
├── hello_samples.yaml
├── hello_samples_<timestamp>/
│ │ .
│ │ .
│ └── .
└── studies/
└── hello_samples_<timestamp>/
│ .
│ .
└── .
Now, let's say we check the status of a study using the hello_samples.yaml spec as input:
Since our original spec file was never modified, the OUTPUT_PATH variable there will still point to the current working directory. Therefore, the above command will look in the current working directory for studies. The output workspace located in the studies/ directory will not be seen.
If we'd like to see the status of the output workspace in the studies directory, we can use the --output-path option:
This will tell the status command to look in the studies/ directory for potential output workspaces associated with the hello_samples.yaml script.
Additionally, to modify the task server from the command line you can use the --task-server option. However, the only currently available
option for task server is celery so you most likely will not want to use this option.
Usage: